CNC Routing Services for Precision Custom Parts
At Sochain Precision, our CNC routing services are designed to support any production requirements.
Means, whether you need a prototype, a short production run, or full-scale manufacturing, the process is structured to give stable quality, predictable lead times, and reliable outcomes.
Rapid prototyping and full-scale production
ISO accredited & QC checks
All in-house processes
Used in over 50 countries
FREE Instant quotations
What Is CNC Routing?
CNC routing cuts a material using a rotating cutter at high speed under controlled programmed instructions. It is an accurate, repeatable, and perfect process when the parts need to fit, assemble, or perform perfectly in the same manner.
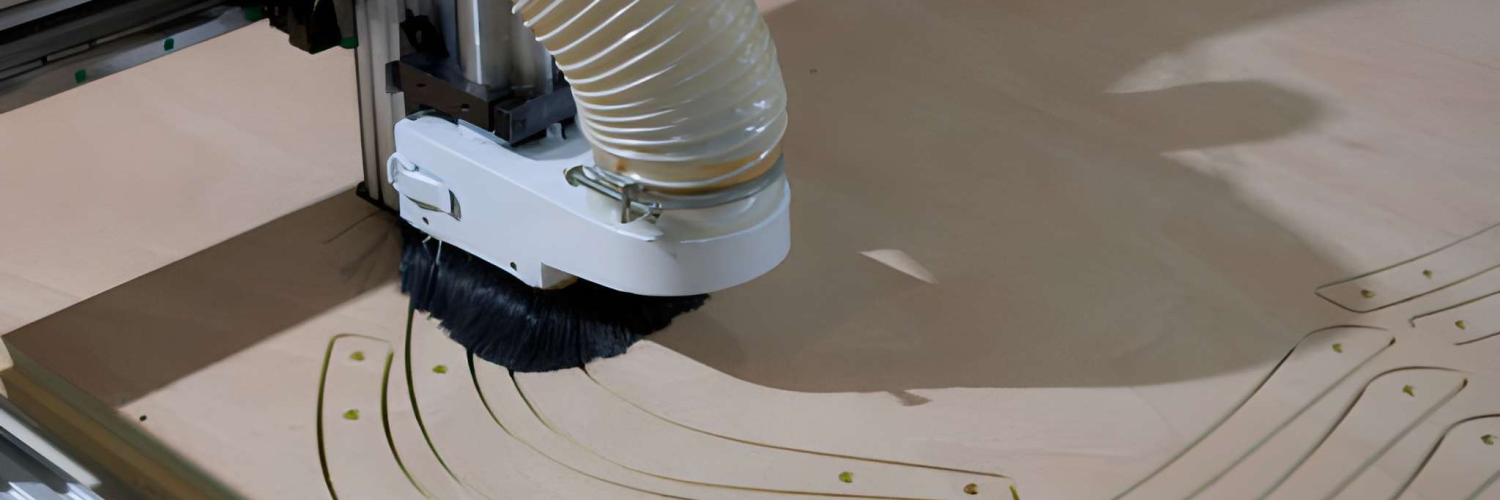

How CNC Routing Works
The process starts with a CAD design. It specifies part geometry, tolerances, and other design details. This design is then translated into toolpaths by CAM software, which determines cutting depth, spindle speed, and feed rate.
The router is moved over a rigid sheet with high precision in cutting profiles, pockets, and internal features. Since the cutting tool is not heat-driven, but mechanically driven, CNC routing does not deform the material and affect the quality of edges.
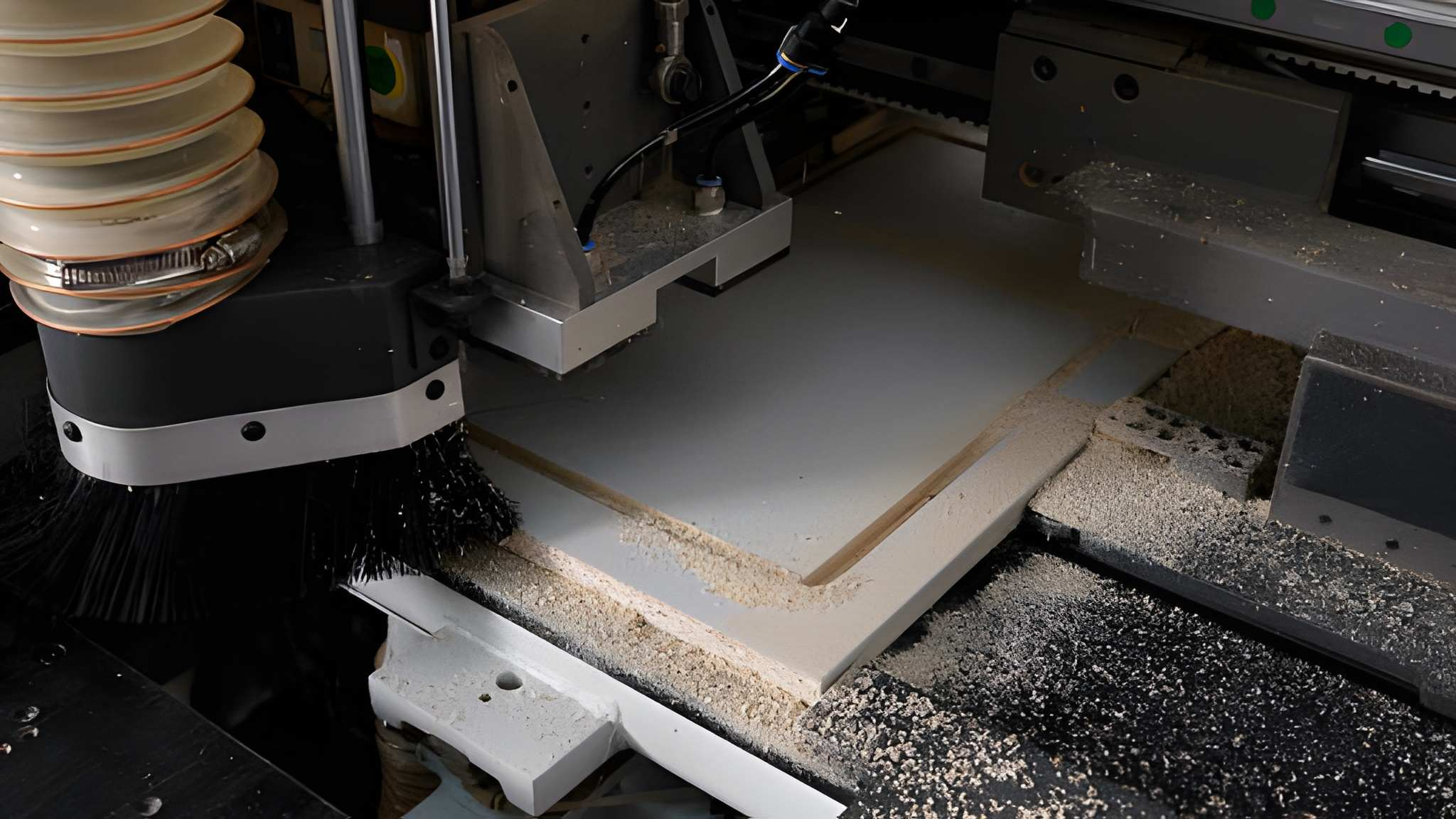

Materials Best Suited for CNC Routing
CNC routing is suitable for materials including:
AcrylicPolycarbonateABSHDPEPVCPlywoodMDFFoams ( HDU (High-Density Urethane/Sign Foam, EPS (Expanded Polystyrene), XPS (Extruded Polystyrene), Polyurethane Tooling Board, EVA Foam (high-density grades)Composite panels (ACM / ACP (Dibond, Alupanel), Gatorfoam, Aluminum Honeycomb Panels, Phenolic Compact Laminate (HPL), Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)These materials cut easily with a controlled cutting speed, and the edge remains clean and consistent when routed in an appropriate manner.
The material thickness is usually between 1 mm and 50 mm, depending on the material choice and the cutting tool.
Note: The materials listed above are commonly CNC routed and are provided for general reference only. If you require a specific material or grade, please contact our team to confirm availability and suitability for your application.
Typical CNC Routing Applications
CNC routing is used to make:
Machine panelsEnclosuresSignageFurniture componentsProtective coversDisplay systemsFunctional industrial and cosmetically finished components
Applications where holes have to be placed consistently, slots need to be precise, or lines must be smooth, CNC routing is a go-to option.
Advantages of CNC Routing Over Manual Cutting
Manual cutting processes often cause variation, edge defects, and alignment issues. CNC routing eliminates these risks as it follows computer-programmed paths precisely, making each and every part resemble the design. Moreover, this enhances the fit of the assembly and minimizes rework.
Our CNC Routing Capabilities
At Sochain Precision, we make complex geometries, large part sizes, and tight production schedules without compromising on precision.
3,4, and 5 Axis CNC Routing
Maximum Part Size and Build Area
Large-format CNC routers are capable of working with sheets up to 30mm x 50 mm x 1500 mm, depending on the material used. This means full-size panels can be cut in one go, so the edges stay clean and the size stays accurate. A larger work area also means fewer joints and less extra work later.
Achievable Tolerances and Accuracy
Generally, CNC routing tolerances are between +/-0.15 mm and +/-0.05 mm for plastic and composites. Stricter tolerances can be obtained on smaller features using stable materials and controlled cutting speeds. During and after machining, critical dimensions are carefully checked.
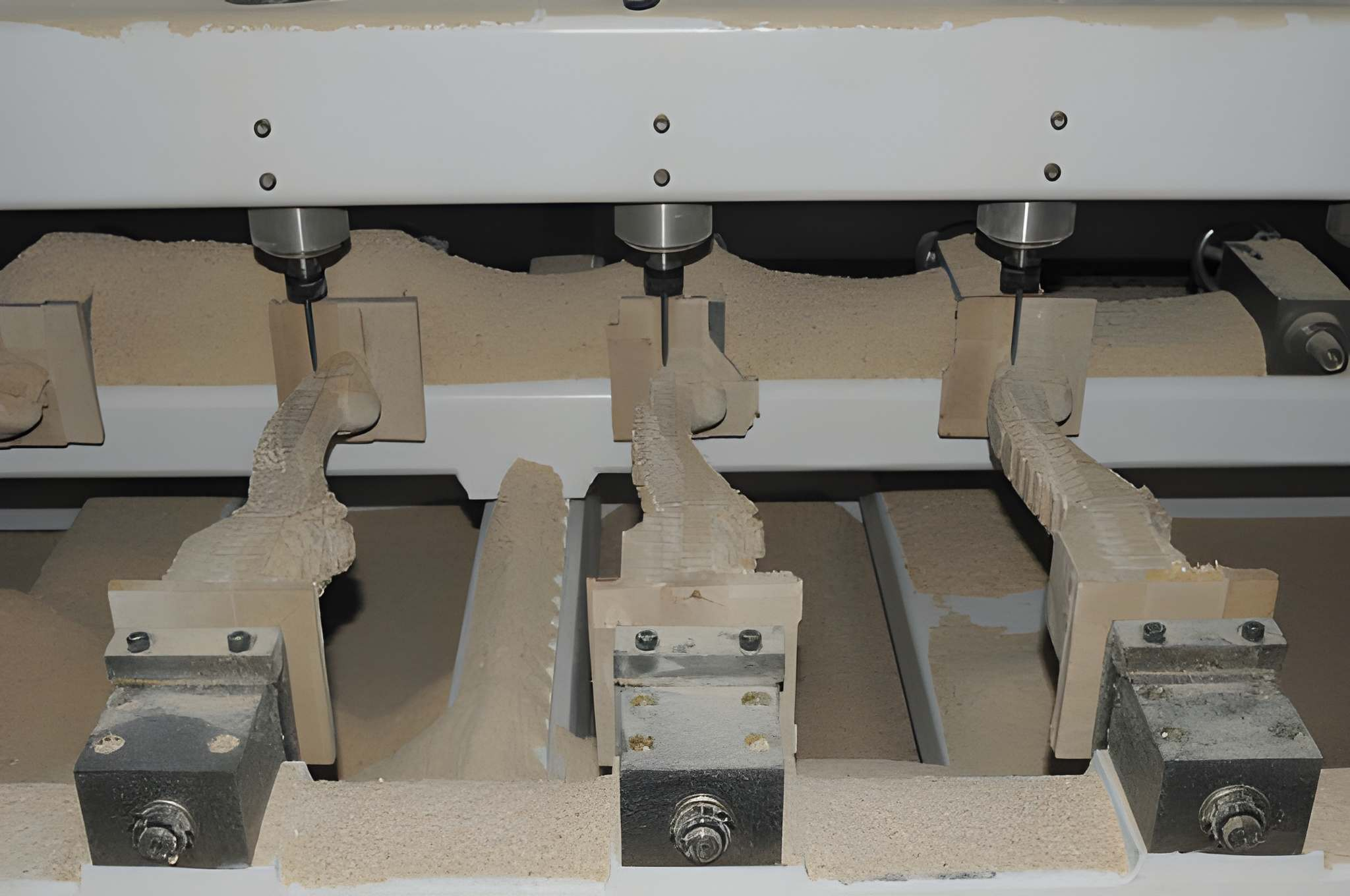

Tooling and Cutter Selection
The choice of the tool is determined by the material type, thickness, and surface finish requirements. A balance between chip evacuation and surface quality is achieved by using single-flute, multi-flute, and compression cutters. Proper tooling eliminates melting, chipping, and tool wear.
Materials We CNC Route at Sochain Precision
The choice of material contributes significantly to the end part quality, and different materials require varied cutting parameters to ensure accuracy and finish.

CNC Routing Plastics
Acrylic, polycarbonate, ABS, nylon, PET, and acetal, among other plastics, are commonly CNC routed at our factory. Feed rates and spindle speeds are optimized to eliminate melting or edges fusing. Automated routing of plastics produces clean edges that can be assembled without issues.
CNC Routing Wood and Sheet Boards
Cabinetry and internal elements of furniture and cabinets are normally made of MDF, plywood, laminated panels, and hardwoods. Grain direction and adhesive content are considered to reduce tear-out and keep the surface smooth during routing. Besides this, good fixturing means the machining is flat all the way through.
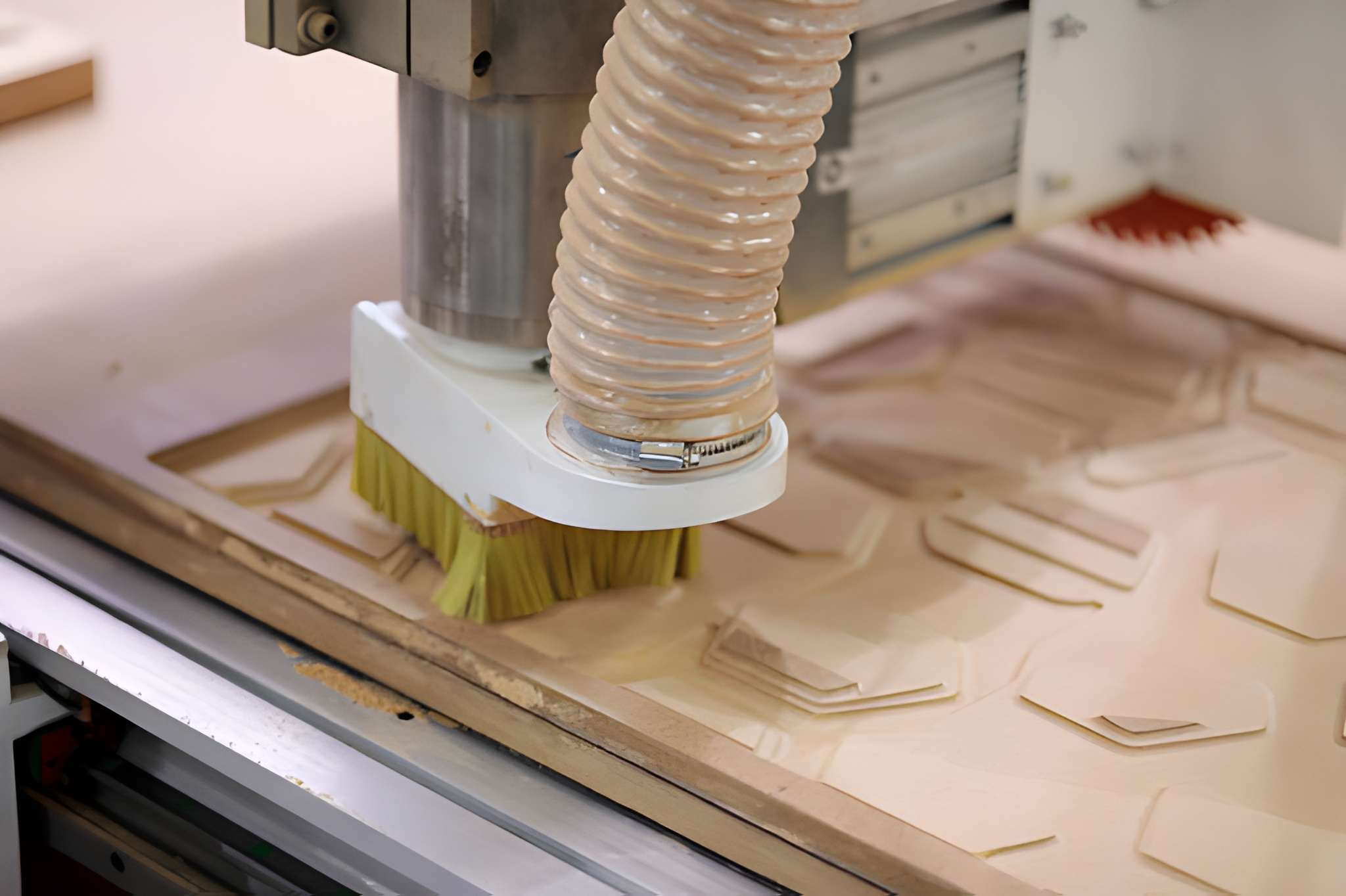


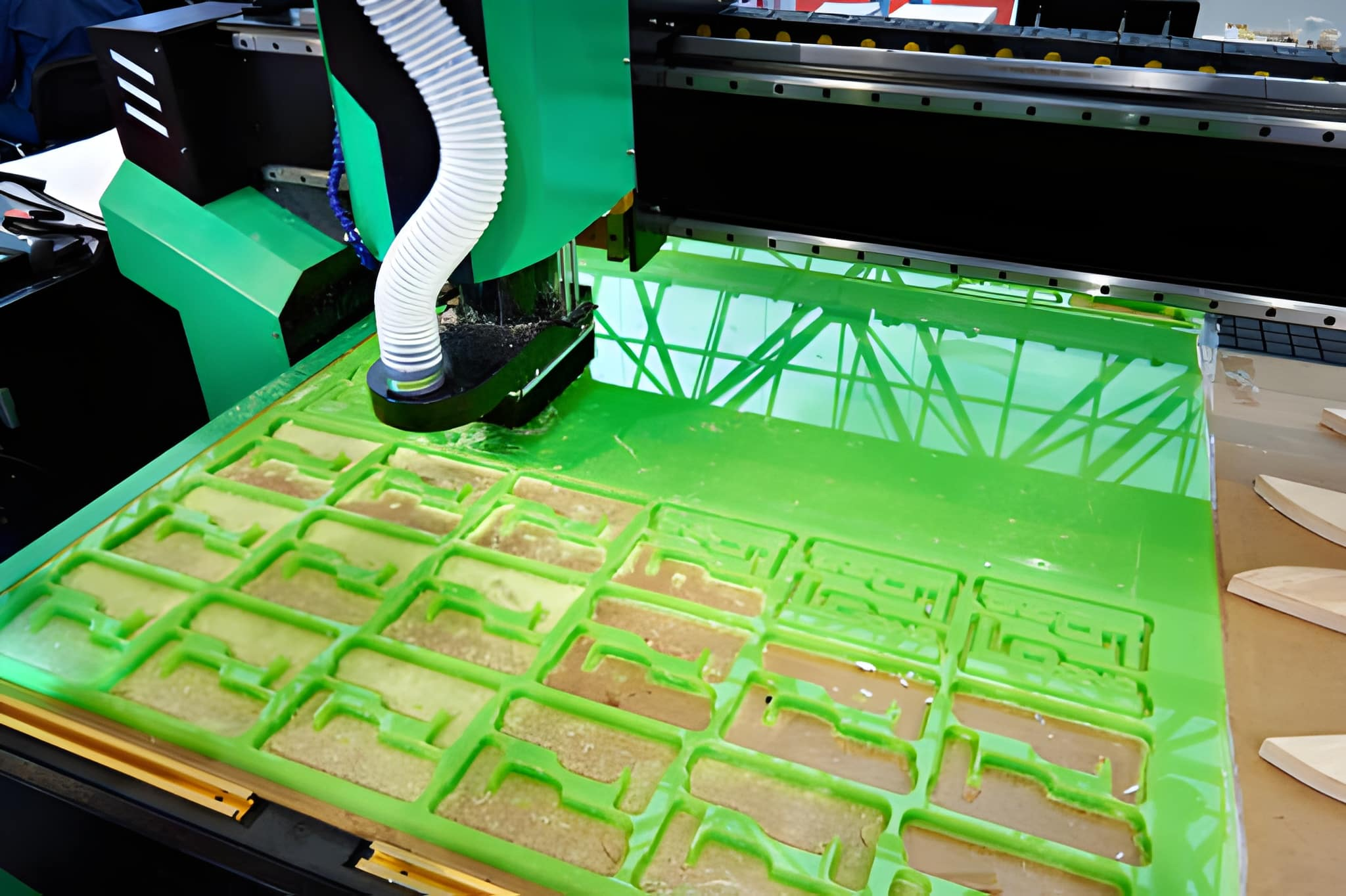
CNC Routing Foams and Composites
Foams and composite materials need less cutting force but constant support. CNC routing generates a clean edge to signage, insulation panels, and structurally lightweight parts. Optimization of tool paths helps avoid delamination.
CNC Routing Soft Metals
Soft metallic materials like aluminum and brass can be routed with specialized cutters and coolant plans. This allows the production of flat metal components without the need for full CNC milling systems.
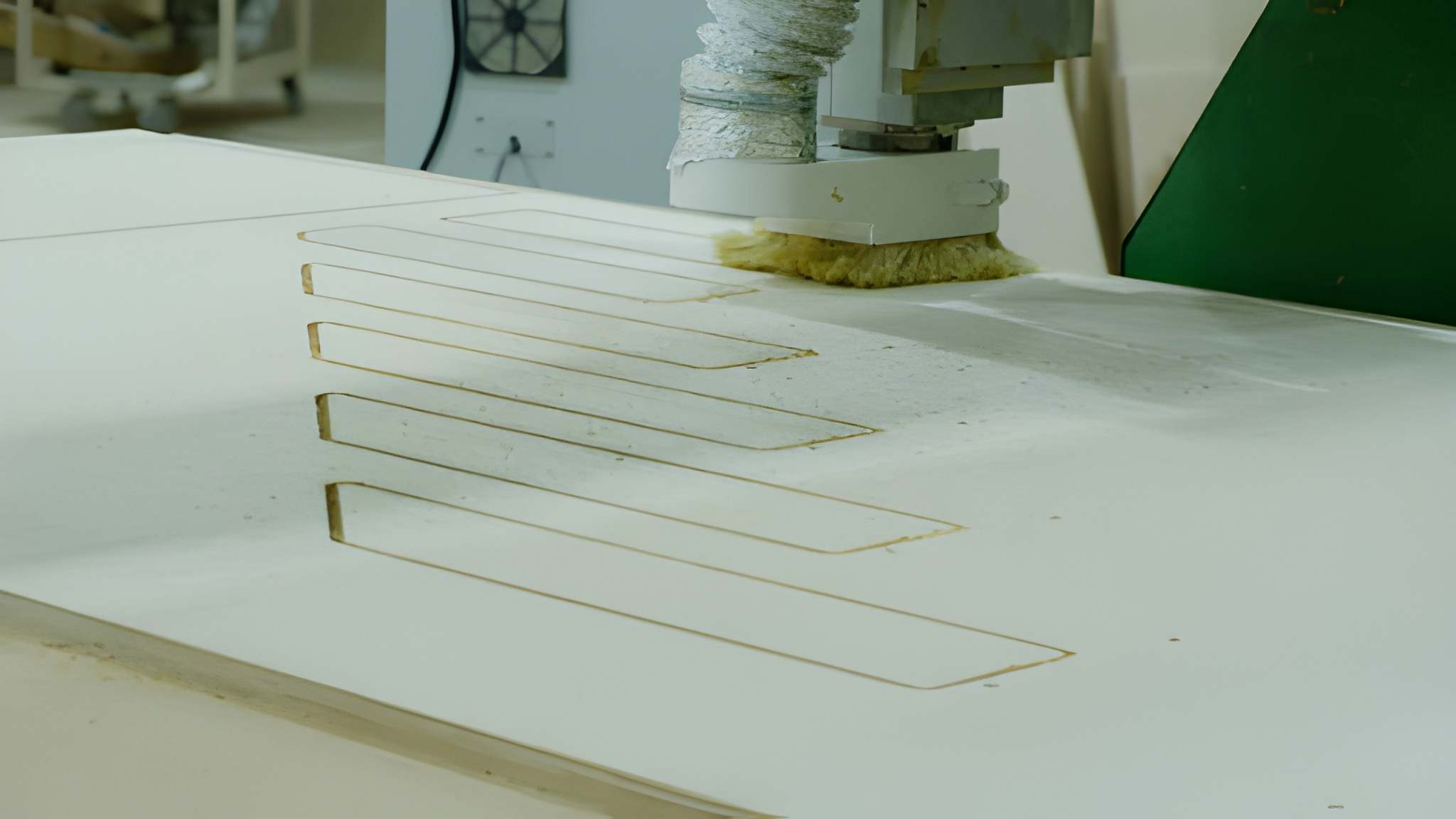

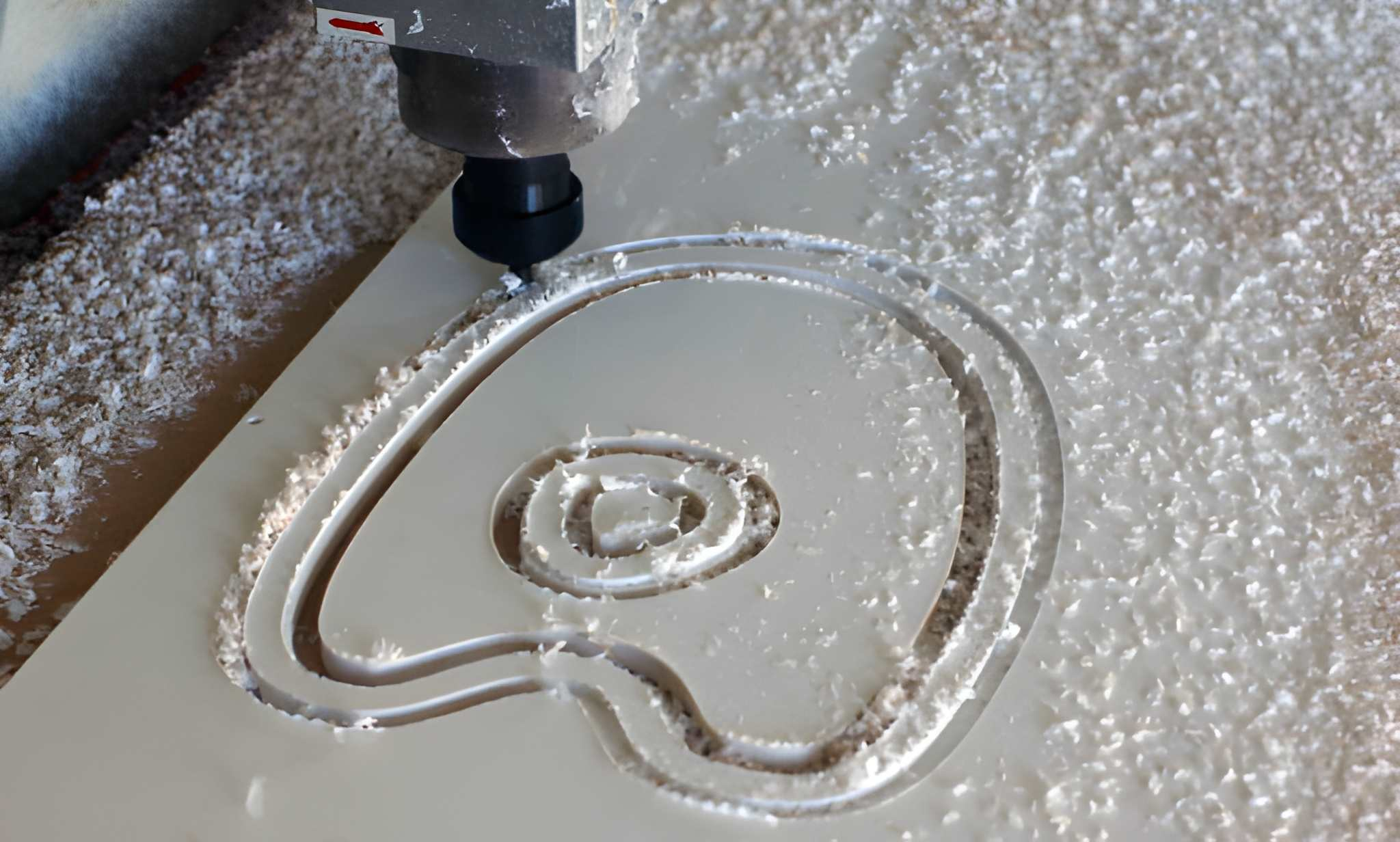
CNC Routing Design Considerations
Good design improves the efficiency in machining and lowers the cost.
Internal Corners and Radii
CNC routers use round cutting tools, so internal corners must include a radius to allow proper cutting. Internal radii typically have a range of 3 mm to 6 mm, depending on the tool size.
Wall Thickness and Stability
It is possible to have thin walls, which may flex during cutting, causing inaccuracy. Having a thick enough wall enhances stability and edge quality, particularly in plastics and foams. Preliminary design review assists in determining the problems that may arise in the future.
Tolerances and Functional Requirements
The tolerances must be based on functional needs. The tight tolerances will add excessive machining time and cost without value addition. Our team assists in balancing the performance and manufacturability.
File Formats and Data Quality
You can send us DXF, DWG, STEP, and IGES file formats. Clear structure, geometry, and well-defined layers minimise programming time and avoid errors.
Our CNC Routing Process
The sequential CNC routing procedure helps prevent errors and maintain consistency between the original cut and the end-use parts.
Design Review and Feasibility Check
A design review is the preliminary step of every project. We inspect material type, sheet thickness, part size, and layouts. Inside corners, slot width, and holes are re-examined to fit available router bits. This avoids the existence of sharp edges that cannot be cut well by tools.
Only when parts need to fit or align, tight tolerances have been used. This ensures efficiency in machining and saves money. When a design requires minor modifications that will improve the quality of cuts or lessen wastage, it is brought up early.
CAM Programming and Toolpath Planning
After the design has been checked, CAM programming comes next. The toolpaths are generated depending on the material behavior and the part complexity. Feed rates, spindle speeds, and cutting depths are chosen to avoid melting, burning, and chipping of the edges.
Part stability is ensured through cutting order. The outer profile is cut last, so the sheet stays rigid and stable throughout the machining process. The accuracy, the cycle time, and possible tool interference of the part are verified through toolpath simulation before the machining.
Machining and In-Process Control
In the CNC routing process, usually, vacuum tables or mechanical fixtures hold parts. On thin sheets or large panels, movement can be prevented by proper holding. Stable setups allow flatness and dimensional accuracy on the whole part.
Key features are checked during machining. If any adjustment is needed, it is made before the full batch is completed. This helps keep every part consistent, not just the first one.
Final Inspection and Approval
The parts are checked to drawings after machining. Dimensions, profiles, and hole positions are inspected to conform to specifications. The surface finish and edge quality are also checked, particularly of visible parts or those that need to be assembled.
Verified parts only pass through finishing or shipment. This will guarantee the customers with CNC-cut parts that are easy to install and that work as desired.
Our Finishing and Secondary Operations
Here are some of the common finishing options available at our facility.
Our Finishing and Secondary Operations
Here are some of the common finishing options available at our facility.
Edge Finishing and Deburring
The edges are cut off or deburred to enhance safety, snugness, aesthetics, and touch.
Drilling, Tapping, and Inserts
Operations such as drilling, tapping, and installing threaded inserts are handled in-house. This avoids outsourcing delays and keeps lead times under control.
Surface Finishing Options
Depending on the material and application, our team uses sanding, polishing, painting, powder-coating, and anodizing to increase the product's life span.
Assembly and Packaging
Assembling, labeling, and packaging of parts is made according to the requirements of the customers, which lowers the product handling once delivered.
Quality Control and Standards
Quality control is our top priority and is involved in each step. Rather than quality checking parts at the end, we inspect parts as we machine them to minimize waste, reduce errors, and maintain consistency throughout.
Dimensional Inspection
Critical dimensions are measured using calibrated tools (digital calipers, micrometers, height gauges, etc.). Characteristics that influence fit or functionality, such as the location of holes, the width of slots, and outer shapes, are given additional focus.
Inspection of the first article is done before the actual production. This ensures that the configuration is right and problems will not occur repeatedly throughout the batch.
Material Verification and Traceability
Every material is checked before starting cutting. We verify that the material type, grade, and thickness are as per the drawing and order requirements.
This step keeps the cuts consistent and helps parts perform as expected, especially in plastics, composites, and aluminum sheets.
Process Control and Records
Machining parameters that include spindle speed, feed rate, tool type, and depth of cut are recorded on each job. These settings are accompanied by inspection results.
Non-Conformance Control
Parts/Components that are not made to the right specifications are isolated. The reason is checked before a production continuation, including tooling, fixturing, and programming. It avoids defects in general and shields the quality of the job.
Continuous Improvement
We check the production results and customer response to make better decisions on tooling, cutting methods, and efficiency of workflow. Minor enhancements with time result in improved finishes on the surface, increased uniformity, and quick turnaround.
Why Choose Our CNC Routing Services
Our CNC routing services focus on reliability, accuracy, and practical manufacturing support. Our engineers combine experience with modern equipment to deliver parts that fit, function, and last longer. Customers value our clear communication, realistic lead times, and consistent quality across every order.
Request a CNC Routing Quote
You simply need to provide your drawings, CAD files, and material requirements. Our team reviews your project and provides a clear, accurate quote based on your machining requirements, not estimates.
FAQs
- What materials can be CNC routed?
CNC routing is commonly used for plastics, wood, MDF, plywood, and composite sheets. Soft metals like aluminum and brass can also be routed. However, they require special tools and optimized cutting speeds. The material selection is usually decided by considering strength, thickness, and how the part will be used.
2. How thick can CNC routing materials be?
Most CNC routing jobs handle materials from about 2 mm to 50 mm thick. Thicker sheets are usually cut in multiple passes to keep the edges neat and accurate. Material type and part size can affect the final thickness limit.
3. Can CNC routing cut complex shapes?
Yes, CNC routing can cut detailed shapes, slots, pockets, and internal cutouts. Curves and repeated patterns are handled with meticulous care.
4. Is CNC routing good for both prototypes and production?
CNC routing works well for prototypes and full production runs. It allows quick changes during testing and consistent results when parts are repeated.
Start Manufacturing Your Custom Parts Now!
Understanding Your Goals, Delivering Your Solutions – We’re Committed to Making CNC Machining Simple and Stress-Free!
